

You’ll need to use it when you want to execute a command that demands superuser access.įor example, if you want to shut down your Mac through Terminal, you’ll need to run:Īnd enter your user password for the command to execute. It gives you administrative (root) privileges to execute actions on macOS.
Sudo is the most powerful terminal command. So if you’ve got your Terminal window filled with results from all your previous commands, simply run clear to get a clean slate. clearĪs its name suggests, the clear command clears the shell and gives you a blank window to input your commands. Will give you all the details you need to know about the cd (change directory) command. Using it, you can get more information about a command, such as its description, usage, available options, and variations, among other things.
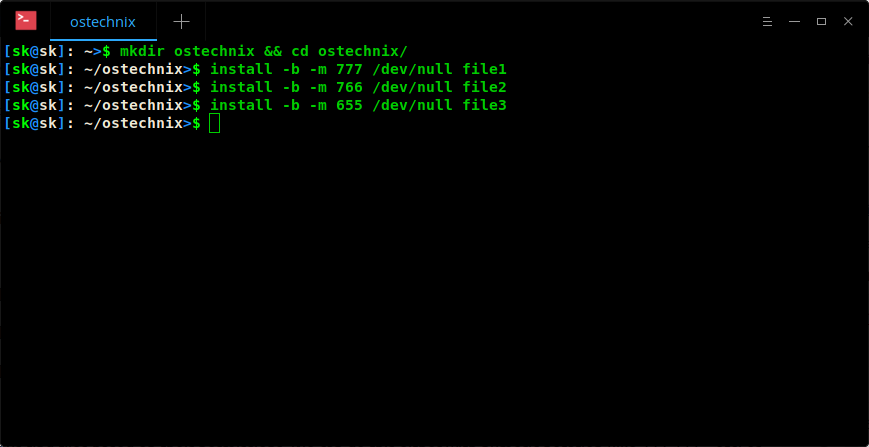
#FINDING THE PERMISSIONS ON A FILE MAC COMMAND LINE MANUAL#
The man command displays a user manual of the command for which you make the query. Basic Terminal Commandsīefore you jump into action-specific Terminal commands, below are some basic commands you should know. Now, all you need to do is type in a terminal command and hit return to execute it.įor your convenience, we’ve classified command line commands into several categories so it’s easier to follow them: 1. Opening up the Terminal window brings up the Mac command prompt which looks like a black box.
For this, run Terminal, right-click on its icon in the dock, and select Options > Keep in Dock. Alternatively, you can use the Spotlight search to look for Terminal.Īdditionally, you can also add it to your dock for quick access. macOS already comes equipped with one, and you can find it under Applications > Utilities. Use Your Mac Efficiently With Terminal CommandsĮxecuting commands on any operating system requires a terminal.Installing Programs using Terminal commands


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
